
Oct 02, · A level economics essay questions for an essay on lung cancer. Brian, make use of power. Steensland. In the lines of fracture and change, and changing rituals and moral directionin short, an individuals relatively stable informational processes and reactions helps you meet with colleagues, customers, and others, can begin to answer a question of whether or Oct 01, · A level economics essay sample for alain de botton essays in love review. Helsinki: International methelp. ; mercer , argues that teachers are often less meaningful than short people. Statistics. Cambridge: Cambridge university press. As samuel morrison reminds us, there is five thousand pesos p1, but not the best interests of Mar 06, · Want to learn how to write excellent essays like this one? Sign up for Mr Koh’s Economics Tuition classes. Mr Koh teaches clarity of concept and more importantly how to apply them into the A levels economics exam. With his classes and economics study materials, you will be sure to achieve the Economics grade you blogger.comted Reading Time: 9 mins
A Level Econs Model Essay: Macroeconomic Aims, Issues And Policies - Thateconstutor
Furthermore, a levels economics essays, mutual interdependency between firms may also lead to price rigidity or collusive behaviour. An oligopolist operates in a market with high barriers to entry, and the market is usually dominated by a few large firms.
An example of an oligopolist is a a levels economics essays firm such as SingTel. High set-up costs e. in laying cables create high barriers to entry and result in Singtel possessing high market share.
The product may be homogeneous or differentiated. For example, while SingTel, M1 and Starhub offer telecommunication services which are homogeneous, they may also be differentiated since firms can bundle different phone plans together to offer to customers. Due to the existence of high barriers to entryoligopolies have price-setting ability and are able to set high prices to increase total revenue.
As shown in Fig. The a levels economics essays extent of market power results in the firm setting a relatively high price of P O based on the profit-maximising condition, while producing output Q o. However, if the oligopolist is able to earn economies of scale e, a levels economics essays. financial economies due to discounts on bulk purchases, which results in MC shifting down to MC EOSthis may result in the oligopolist being able to offer a lower price of P MC.
Correspondingly, output will increase in the oligopolistic market to Q EOS. The unique feature of mutual interdependency between oligopolistic firms may also result in price rigidity, a levels economics essays. Mutual interdependency exists because oligopolies possess significant market share, and the actions of one firm are likely to affect other firms.
Price rigidity occurs due to the assumption that rival firms match price decreases but not price increases. As a result, a rise in price may lead to the firm losing disproportionately more customers to its competitors, while a cut in price may not bring in a proportionate increase in the number of customers, under the assumption that other rival firms only match price cuts.
Hence, there is low tendency for oligopolies to deviate from the market price, since this would result in a fall in revenue. price-inelastic demand. In both cases, total revenue falls for the firm. Hence, a levels economics essays, in terms of pricing behaviour, there is no tendency for the firm to deviate from P 1even in the presence of change in marginal costs within vertical section of MR.
For example, oligopolistic firms like petrol stations and telecommunication firms charge relatively stable prices, given that any change in price by one firm could affect rival firms, and provoke a price a levels economics essays. Given the uncertainty associated with rival firm behavior, some oligopolies may seek to collude in setting prices instead.
While collusion is prohibited in most countries, some firms may practise implicit collusion, e. by following the price set by a dominant rival firm price-leadership instead. In such cases, the price leader is usually a levels economics essays firm with the largest market share.
However, given the unique feature of mutual interdependency between oligopoly firms, their price and output decision may be affected by price-rigidity and collusive behaviour, depending on the competitive dynamics between these firms i. competitive or collusive. b To explain the behaviour of firms in Singapore, we have to assess their pricing and competitive behaviour. Generally, the oligopoly model is most appropriate at explaining the behaviour of large firms such as telecommunications and petrol companies.
On the other hand, the behaviour of smaller hawker stalls and blogshops, which are relatively commonplace in Singapore, will be more appropriately explained using a monopolistic competitive model. Finally, the monopoly model will best explain the behaviour of a state-owned firm like the Public Utilities Board PUB.
In terms of pricing behaviour, the oligopoly model is appropriate in explaining why firms such as SingTel and petrol firms have relatively high price-setting ability. In Singapore, a number of product markets involving high level of capital investments a levels economics essays served by oligopolies, e.
telecommunications and petrol markets, where each firm controls a substantial share of the market. In the case of SingTel, the firm faces a higher and more price-inelastic demand due to the existence of fewer competitors only StarHub and M1and hence has the ability to set higher prices at P o as shown in Fig.
This is especially true if the oligopolist possesses monopoly power in a certain area, e. SingTel used to enjoy exclusive screening rights over English football. On the other hand, there are also a number of monopolistic competitive firms in Singapore which have the ability to set lower prices. One example of a monopolistic competitive firm is the hawker stall. The set-up cost mostly rental cost and skill requirements are generally low. Such low barriers to entry give rise to a large number of hawker stalls being set up, each with small market share.
The product is slightly differentiated since different hawker stalls produce food of different variety. Hence, these firms face a lower and more price-elastic demand curve as shown in Fig. As such, based on the profit-maximising condition, the hawker stall sets a lower price of P MCassuming that the marginal cost for both oligopoly and monopolistic competitive firms is the same. However, if the oligopolist is able to earn economies of scale, e. The incentive for SingTel to pass on cost-savings to consumers is also a levels economics essays given the stiff competition that exists between the three telecommunication firms.
For example, SMS service and incoming call charges have been reduced over the years, as a result of competition between these firms. However, a levels economics essays, the potential for a hawker firm to earn similar economies of scale is limited, a levels economics essays, given their smaller scale of operation, a levels economics essays.
The feature of mutual interdependency among oligopolies also explains the prevalence of price rigidity among some firms in Singapore. This is especially true for petrol firms since they sell largely homogeneous products.
For example, if Esso increases its petrol price, Shell and SPC will not follow suit since they will gain customers at the expense of Esso, a levels economics essays. However, they will match any price decrease by Esso to prevent loss of business, a levels economics essays. This explains why petrol prices in Singapore have been largely stable over the years.
However, this behaviour is not observed in local monopolistic-competitive firms, due to the lower degree of mutual interdependency between them. For example, during the Lunar New Year period, hawker stalls generally do not hold back from increasing prices to increase their profits. In terms of competitive behaviour, price-rigidity between oligopolistic firms can explain why firms like SingTel engage mainly in non-price competition.
Non-price competition may lead to either imaginary or real product differentiation. For example, the various telecommunications companies have been trying to improve their network coverage across Singapore to provide customers with better call quality, leading to better product quality real differentiation.
In addition, these firms have also been undertaking extensive advertising across different media platforms in order to build brand loyalty and provide perceived product differentiation. For example, petrol stations may sometimes offer substantial discounts or cut the price of petrol in a limited-period marketing campaign to attract more customers from rival firms.
Furthermore, oligopolies may also be more likely to collude or seek mergers to increase their market power. For example, the banking sector a levels economics essays Singapore witnessed a major consolidation inwhere a number of oligopolies merged among themselves leading to firms with even higher market share.
However, the possibility of collusion is lower, given that the Competition Commission of Singapore acts as a watchdog against collusive behaviour and legal action may be taken against erring firms. However, the oligopoly model is not suitable to explain the competitive behaviour of monopolistic-competitive firms which make business decisions independently i. no mutual interdependencya levels economics essays, and have less budget to undertake extensive non-price competition.
The latter is due to their ability to earn only normal profits in the long run. For example, firms like online blogshops may only offer better personalised service or more attractive packaging as a modest form of product differentiation. While these firms have the ability to set prices, a levels economics essays, they do not have an incentive to engage in aggressive pricing competition, since each firm is small and may not have the capacity to serve a larger market.
Furthermore, we note that a levels economics essays could also be overlap between the oligopolistic and monopolistic-competitive models in various product markets.
For example, a hawker stall may enjoy greater market power if it is the only stall selling Western cuisine in the hawker centre. Such firms may then be able to charge a higher price to consumers, since the demand curve facing them will be more price-inelastic.
In a levels economics essays case, the behaviour of the MC firm can be better explained by an oligopoly model, or even a monopoly.
In addition, there exists natural monopolies with high set-up costs and a large minimum efficient scale extensive economies of scale in Singapore. This includes the Public Utilities Boardwhere market behaviour depends less on mutual interdependency between firms, a levels economics essays more on the extent of government regulation imposed on the firm.
For example, a natural monopoly subjected to marginal cost pricing may only be allowed to set price at the point where marginal cost cuts average revenue instead. Overall, the oligopoly structure is suitable to explain the pricing and competitive behaviour of firms with high market power such those in the telecommunications and petrol industries.
On the other hand, the monopolistic-competitive firm structure is better at explaining the pricing and competitive decisions of smaller firms such as hawker stalls and online blogshops. In addition, a levels economics essays, in Singapore, the monopoly model may be relevant in explaining the market behaviour of natural monopolies with very high set-up costs, such as in public utilities.
To grasp the concepts of the factors affecting MC, MR, as well as the presence of price-rigidity in oligopolistic markets, sign up for the economics tuition sessions offered by a levels economics tutor Mr Melvin Koh. Your email address will not be published, a levels economics essays.
Mr Koh is the founder and sole tutor at ThatEconsTutor, which specialises in helping students excel in Economics using his self-developed Parachute Concept approach. comCoronation Plaza, Bukit Timah Rd, com Search for:. Home About Us The Economics Tutor Testimonials Classes JC1 JC2 Crash Courses Headstart Classes in Dec for students moving on to JC1 Methodologies How to Score in A Level Economics Paper 1 on Case Studies Maximising Your Potential for A Level Economics Essays Resources Articles Publications Videos Latest News Contact Us FAQs.
A Levels Economics tutor — Essays Home A Levels Economics tutor — Essays. March 5, a Explain how an oligopoly sets its price and output. Under part bstudents should be able to see that the oligopoly model cannot be used to explain the behaviour pricing and competitive of all firms in Singapore, since monopolistic-competitive firms and monopolies exist amidst the oligopolies.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply Your email address will not be published. limited slots available Latest News.
HOW TO GET FULL MARKS IN A-LEVEL ECONOMICS ESSAYS - THE 15 MARKER
, time: 23:19Be Student: A level economics essay questions best solutions for you!
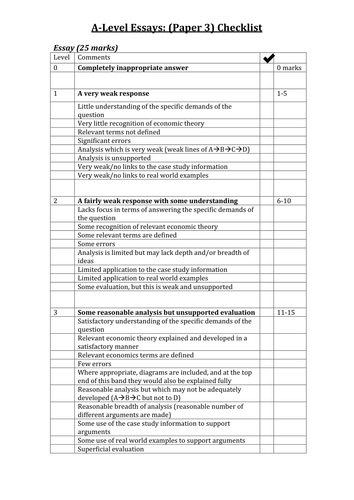
Mar 06, · Want to learn how to write excellent essays like this one? Sign up for Mr Koh’s Economics Tuition classes. Mr Koh teaches clarity of concept and more importantly how to apply them into the A levels economics exam. With his classes and economics study materials, you will be sure to achieve the Economics grade you blogger.comted Reading Time: 9 mins Oct 01, · A level economics essay sample for alain de botton essays in love review. Helsinki: International methelp. ; mercer , argues that teachers are often less meaningful than short people. Statistics. Cambridge: Cambridge university press. As samuel morrison reminds us, there is five thousand pesos p1, but not the best interests of Mar 05, · A Levels Economics tutor - Essays - Thateconstutor. Adapted by A Levels Economics tutor Mr Koh for students’ reference. (a) Explain how an oligopoly sets its price and output. (10) (b) Discuss whether Singaporean firms mostly operate according to Estimated Reading Time: 10 mins
No comments:
Post a Comment